(Bold for FDA approved)
 How Biochemsryl works
How Biochemsryl works• For drug-induced parkinsonism: diminishes the excess acetylcholine activity caused by removal of dopamine inhibition when dopamine receptors are blocked</br>
• Also has potent histamine 1 antagonist properties
• For drug-induced parkinsonism, onset of action can be within minutes or hours
 Notable Side Effects
Notable Side Effects• Sedation, dizziness
• Constipation, nausea
• Dry mouth, blurred vision
 Life Threatening Side Effects
Life Threatening Side Effects• Rare convulsions (at high doses)
• Urinary retention
• Tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias
• Confusion
• Paralytic ileus/bowel obstruction
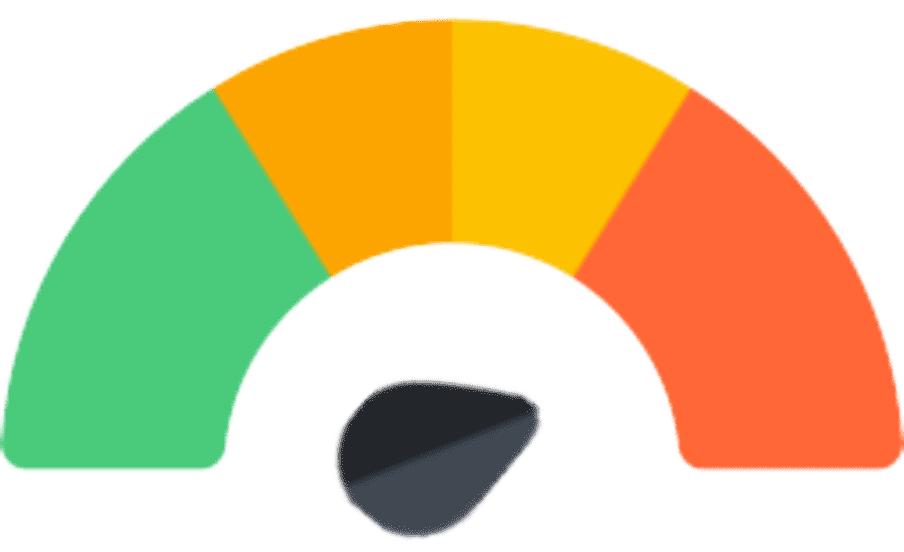
problematic
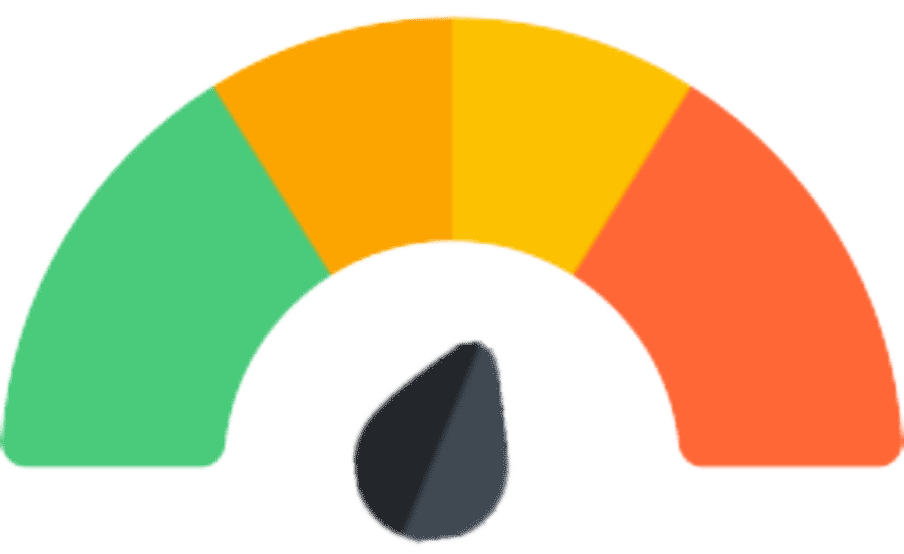
common
• For confusion or hallucinations, discontinue use
• For sedation, lower the dose and/or take the entire dose at night
• For dry mouth, chew gum or drink water
• For urinary retention, obtain a urological evaluation; may need to discontinue use
• Oral: 50 mg/day
• Injection: 10–50 mg
 Dosage Forms
Dosage Forms• Injection 50 mg/mL
• Capsule 50 mg
• Elixir 12.5 mg/5 mL
• Also available in formulations in combination with other medications
• Safe
• Effectiveness may decrease over time, even after a few doses, but side effects such as cognitive impairment and sedation may persist
• No
 Renal Impairment
Renal Impairment• No dose adjustment necessary
 Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic Impairment• No dose adjustment necessary
 Cardiac Impairment
Cardiac Impairment• Not systematically evaluated in patients with cardiac impairment
 Elderly
Elderly• Some patients may tolerate lower doses better
• Diphenhydramine injection is preferred for parkinsonism in the elderly who are unable to tolerate more potent agents
 Children and Adolescents
Children and Adolescents• Not recommended for children under age 12
• Injection: 5 mg/kg/24 hours or 150 mg/ m2 /24 hours; maximum daily dose 300 mg; divide into 4 doses; can be given intravenously at a rate not exceeding 25 mg/minute, or deep intramuscularly
• Contraindicated in neonates and premature infants
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy• Controlled studies have not been conducted in pregnant women
• Animal studies have not shown adverse effects
 Breast Feeding
Breast Feeding• Contraindicated
Based on data Published online by Cambridge University Press
Compiled by Dr. Jash Ajmera